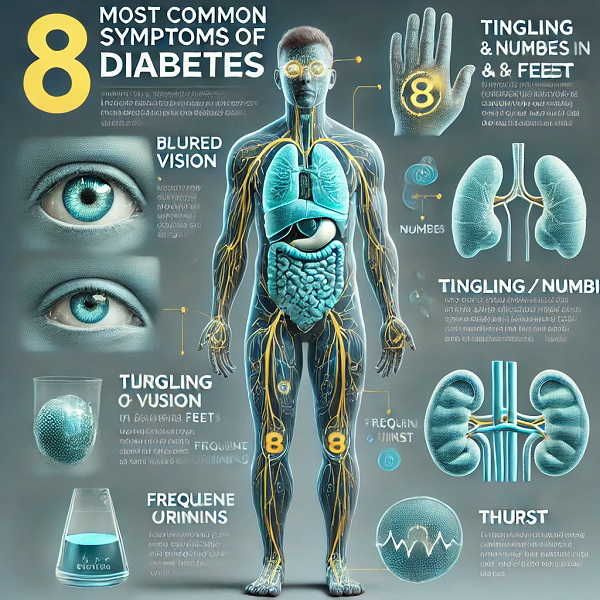
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy. The majority of the food we eat is broken down into sugar (glucose) and released into our bloodstream. When blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas is signaled to release insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get into your body’s cells to be used for energy. However, in diabetes, the body either doesn’t make enough insulin or can’t use the insulin it makes as well as it should. This leads to too much blood sugar staying in your bloodstream, which can cause serious health problems over time, such as heart disease, vision loss, and kidney disease. Early detection of diabetes is crucial in managing the condition effectively. Here are the eight most common symptoms of diabetes that everyone should be aware of.
1. Frequent Urination (Polyuria)
One of the earliest and most noticeable symptoms of diabetes is frequent urination, known medically as polyuria. This occurs when the kidneys filter excess sugar from your blood, which pulls more water into the urine. People with diabetes may find themselves needing to urinate more frequently, particularly at night. This can disrupt sleep and lead to fatigue.
When blood glucose levels are too high, your kidneys try to remove the excess sugar by filtering it out of the blood, resulting in a high volume of urine. The constant need to urinate can also lead to dehydration, creating a vicious cycle of thirst and urination.
2. Increased Thirst (Polydipsia)
Following closely on the heels of frequent urination is increased thirst, medically known as polydipsia. As the body loses fluids through frequent urination, it naturally tries to replace the lost fluids, leading to an unquenchable thirst. No matter how much you drink, it seems impossible to satisfy this thirst.
Polydipsia is a direct response to dehydration caused by excessive urination. The more you urinate, the more fluids you need to drink to replace what you’ve lost. This is the body’s way of trying to maintain fluid balance, but in diabetes, it often feels like a losing battle.
3. Extreme Hunger (Polyphagia)
Diabetes affects your body’s ability to use glucose for energy. When your cells are deprived of glucose, they send signals to the brain that they need more energy, leading to feelings of extreme hunger, known as polyphagia. This can occur even after you’ve just eaten, as your body is unable to convert the food you consume into energy efficiently.
Polyphagia can be particularly frustrating for people with diabetes because, despite eating more, they may continue to lose weight. The body is essentially starving for energy, leading to increased appetite and food consumption, but without the usual benefits of feeling satiated.
4. Unexplained Weight Loss
Unexplained weight loss is a common symptom of diabetes, particularly in type 1 diabetes. Despite eating more than usual to quell hunger, people with diabetes may experience weight loss. This happens because the body cannot properly use glucose for energy and begins to break down fat and muscle tissue for fuel instead.
In type 1 diabetes, the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to little or no insulin production. Without insulin, glucose cannot enter the cells, leading to starvation at the cellular level, which prompts the body to start burning fat and muscle for energy, resulting in weight loss.
5. Fatigue
Fatigue is another common symptom of diabetes. When the body can’t use glucose properly for energy, it can leave you feeling tired and weak. This lack of energy can affect your daily life, making it difficult to perform even the simplest tasks.
There are several reasons why diabetes causes fatigue. High blood sugar levels can impair your body’s ability to convert glucose into energy. Moreover, the frequent urination associated with diabetes can lead to dehydration, which can also make you feel tired. Additionally, managing the disease itself can be mentally and physically exhausting.
6. Blurred Vision
Blurred vision is a common symptom of diabetes that occurs when high blood sugar levels cause the lens of the eye to swell, changing its shape and flexibility. This can make it difficult to focus, leading to blurred vision.
Over time, if blood sugar levels remain high, it can cause damage to the blood vessels in the retina, leading to more severe vision problems such as diabetic retinopathy. Regular eye exams are crucial for people with diabetes to catch and treat any vision problems early on.
7. Slow Healing of Wounds
Diabetes can affect your body’s ability to heal wounds. High blood sugar levels can impair the function of white blood cells, which are essential for healing wounds. Additionally, diabetes can cause poor circulation, making it harder for blood to reach the affected area and slow down the healing process.
This is particularly dangerous because even small cuts or blisters can develop into serious infections if they are not treated promptly. People with diabetes are at higher risk for developing ulcers, particularly on their feet, which can lead to severe complications if left untreated.
8. Tingling or Numbness (Neuropathy)
Tingling or numbness in the hands and feet, known as neuropathy, is a common symptom of diabetes. High blood sugar levels can cause damage to the nerves over time, leading to a loss of sensation or pain in the affected areas.
Peripheral neuropathy is the most common type of diabetic neuropathy and usually affects the legs and feet first. It can lead to a range of symptoms, including pain, burning, tingling, and loss of coordination. In severe cases, it can lead to foot ulcers, infections, and even amputation.
Importance of Early Detection and Management
Recognizing the symptoms of diabetes early is crucial for preventing serious complications. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Early intervention can help manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a serious condition that requires careful management to prevent complications. By being aware of the common symptoms, such as frequent urination, increased thirst, extreme hunger, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, slow healing of wounds, and tingling or numbness, you can take proactive steps to manage your health. Early detection and treatment are key to living a healthy life with diabetes.
References:
- American Diabetes Association: Signs and Symptoms of Diabetes
- Mayo Clinic: Diabetes Symptoms
- WebMD: Understanding Diabetes Symptoms
#diabetesawareness #diabetessymptoms #health #wellness #diabetescare #healthyliving #diabetesmanagement #chronicillness #diabetessupport #knowyourdiabetes