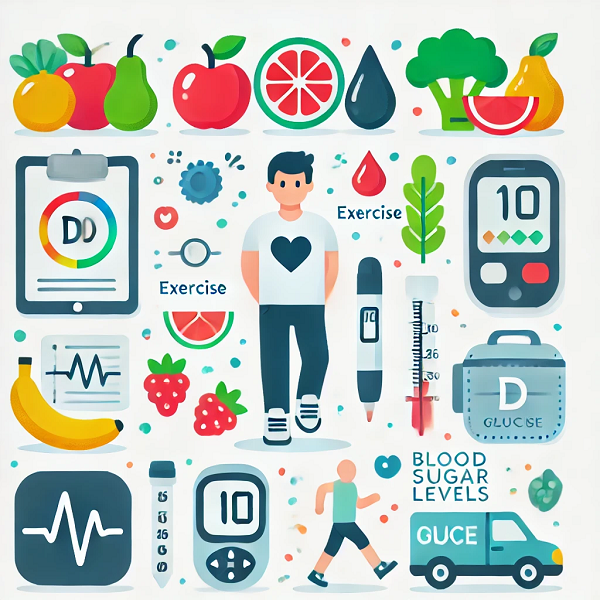
Managing diabetes effectively is a critical aspect of maintaining overall health and preventing serious complications. One of the most vital components of diabetes management is regular blood glucose monitoring. This practice involves frequently checking blood sugar levels to ensure they remain within a target range. Regular blood glucose monitoring provides individuals with valuable information about their blood sugar levels and helps them make informed decisions about their diet, medication, and lifestyle. This article explores the importance of regular blood glucose monitoring and its benefits for individuals with diabetes.
Understanding Blood Glucose Monitoring
Blood glucose monitoring involves using a blood glucose meter to measure the amount of glucose in a small sample of blood. This process helps individuals with diabetes track their blood sugar levels and make necessary adjustments to maintain them within a healthy range. Regular monitoring is essential for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes management. It provides immediate feedback on how well the treatment plan is working and helps identify patterns and trends in blood sugar levels.
Benefits of Regular Blood Glucose Monitoring
1. Improved Glycemic Control
One of the primary benefits of regular blood glucose monitoring is improved glycemic control. By frequently checking blood sugar levels, individuals can identify high or low levels and take corrective actions promptly. This proactive approach helps maintain blood sugar levels within the target range, reducing the risk of hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Improved glycemic control is crucial for preventing diabetes-related complications, such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and retinopathy.
2. Personalized Diabetes Management
Diabetes management is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Regular blood glucose monitoring allows individuals to personalize their treatment plans based on their unique needs and responses to different interventions. For example, monitoring blood sugar levels before and after meals can help determine the impact of specific foods on blood glucose. This information enables individuals to make informed dietary choices and adjust their meal plans accordingly. Additionally, regular monitoring helps healthcare providers tailor medication dosages and treatment regimens to achieve optimal glycemic control.
3. Early Detection of Blood Sugar Fluctuations
Blood sugar levels can fluctuate due to various factors, including diet, physical activity, stress, illness, and medication. Regular monitoring allows individuals to detect these fluctuations early and take appropriate actions to prevent severe hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. For instance, monitoring blood sugar levels during periods of illness or stress can help identify patterns and implement necessary adjustments to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Early detection of blood sugar fluctuations is essential for preventing acute complications, such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and severe hypoglycemia.
4. Enhanced Understanding of Diabetes
Regular blood glucose monitoring provides individuals with valuable insights into their diabetes management. By tracking blood sugar levels over time, individuals can identify trends and patterns that can help them understand how different factors affect their blood glucose. This enhanced understanding empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their lifestyle, diet, and medication. Additionally, it promotes a proactive approach to diabetes management, encouraging individuals to take control of their health and make necessary adjustments to achieve better outcomes.
5. Prevention of Long-Term Complications
Effective diabetes management aims to prevent long-term complications associated with uncontrolled blood sugar levels. Regular blood glucose monitoring plays a crucial role in achieving this goal. By maintaining blood sugar levels within the target range, individuals can reduce the risk of developing complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems. Regular monitoring also helps healthcare providers identify early signs of complications and implement appropriate interventions to prevent their progression.
Best Practices for Blood Glucose Monitoring
To maximize the benefits of regular blood glucose monitoring, individuals with diabetes should follow best practices and guidelines recommended by healthcare professionals. Here are some essential tips for effective blood glucose monitoring:
1. Monitor Frequently
The frequency of blood glucose monitoring depends on various factors, including the type of diabetes, treatment plan, and individual needs. Healthcare providers typically recommend monitoring blood sugar levels multiple times a day, including before and after meals, before bedtime, and during periods of illness or stress. Frequent monitoring provides a comprehensive picture of blood sugar trends and helps identify patterns that can guide treatment adjustments.
2. Use Reliable Monitoring Devices
Using reliable and accurate blood glucose monitoring devices is essential for obtaining precise readings. Individuals should choose a blood glucose meter that meets their needs and preferences. It is also important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper use and maintenance of the device. Regular calibration and quality control checks can help ensure accurate readings and reliable results.
3. Keep a Blood Glucose Log
Maintaining a blood glucose log is a valuable practice for tracking blood sugar levels and identifying patterns. Individuals should record their blood sugar readings, along with relevant information such as the time of day, meals, physical activity, and medication. This log can be shared with healthcare providers during appointments to facilitate discussions and make informed decisions about diabetes management.
4. Understand Target Ranges
Understanding target blood glucose ranges is crucial for effective diabetes management. Healthcare providers typically establish individualized target ranges based on factors such as age, type of diabetes, overall health, and treatment goals. Individuals should aim to keep their blood sugar levels within these target ranges to reduce the risk of complications. Regular monitoring helps identify deviations from the target range and allows for prompt corrective actions.
5. Communicate with Healthcare Providers
Regular communication with healthcare providers is essential for optimal diabetes management. Individuals should share their blood glucose logs and any concerns or questions with their healthcare team during appointments. Healthcare providers can offer valuable insights, make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan, and guide managing blood sugar levels effectively. Open and honest communication fosters a collaborative approach to diabetes management and improves overall outcomes.
Addressing Common Challenges in Blood Glucose Monitoring
Despite its importance, regular blood glucose monitoring can present challenges for some individuals. Addressing these challenges is crucial for maintaining consistent monitoring and achieving optimal glycemic control. Here are some common challenges and strategies to overcome them:
1. Fear of Needles
Fear of needles is a common barrier to regular blood glucose monitoring. To address this challenge, individuals can explore alternative monitoring methods, such as continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems. CGM devices use a sensor inserted under the skin to measure blood glucose levels continuously. These devices provide real-time data without the need for frequent finger pricks. Additionally, seeking support from healthcare providers and mental health professionals can help individuals overcome their fear of needles and develop a positive attitude toward blood glucose monitoring.
2. Busy Lifestyles
A busy lifestyle can make it challenging to find time for regular blood glucose monitoring. To overcome this challenge, individuals can establish a routine and incorporate monitoring into their daily schedule. Setting reminders on smartphones or using apps designed for diabetes management can help individuals stay on track. Additionally, involving family members or caregivers in the monitoring process can provide support and ensure consistency.
3. Cost of Monitoring Supplies
The cost of blood glucose monitoring supplies, such as test strips and lancets, can be a financial burden for some individuals. To address this challenge, individuals can explore options such as insurance coverage, patient assistance programs, and discounts offered by manufacturers. Healthcare providers can also provide guidance on cost-effective monitoring strategies and recommend affordable monitoring devices.
4. Inaccurate Readings
Inaccurate blood glucose readings can undermine the effectiveness of monitoring and lead to incorrect treatment decisions. To ensure accurate readings, individuals should follow best practices for blood glucose monitoring, including proper handwashing before testing, using fresh test strips, and calibrating the meter regularly. It is also important to address any technical issues with the monitoring device promptly and seek assistance from healthcare providers if needed.
Conclusion
Regular blood glucose monitoring is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management. It provides individuals with valuable information about their blood sugar levels, enabling them to make informed decisions about their diet, medication, and lifestyle. The benefits of regular monitoring include improved glycemic control, personalized diabetes management, early detection of blood sugar fluctuations, enhanced understanding of diabetes, and prevention of long-term complications. By following best practices and addressing common challenges, individuals with diabetes can achieve optimal glycemic control and lead healthier lives. Regular blood glucose monitoring empowers individuals to take control of their diabetes and make proactive choices for better health outcomes.
References:
- American Diabetes Association – Monitoring Your Blood Sugar
- Mayo Clinic – Diabetes Management: How Lifestyle, Daily Routine Affect Blood Sugar
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases – Blood Glucose Monitoring
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – Managing Diabetes
- Johns Hopkins Medicine – Blood Sugar Monitoring
Other Important Articles:
- Innovative Treatments for Diabetes You Need to Know About
- Diabetes Management: Tips For A Healthier Lifestyle
- The Best Apps Available to Help You Manage Diabetes
#diabetesmanagement #bloodsugarcontrol #glycemiccontrol #diabetescare #bloodglucosemonitoring #health #wellness #diabetesawareness #preventdiabetes #healthyliving