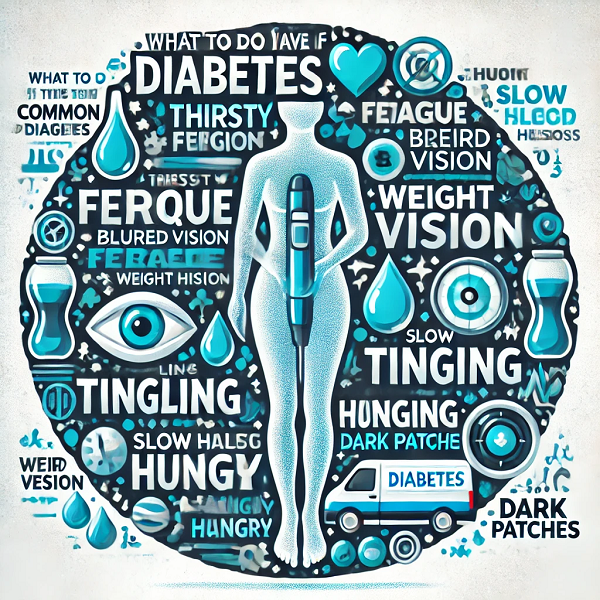
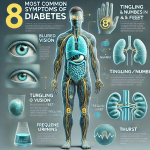
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It’s essential to recognize the early signs and symptoms of diabetes so that you can seek prompt medical attention and prevent complications. This article will walk you through what to do if you experience eight common symptoms of diabetes, helping you take control of your health.

1. Excessive Thirst and Frequent Urination
One of the hallmark symptoms of diabetes is excessive thirst, medically known as polydipsia, accompanied by frequent urination (polyuria). This occurs because excess glucose builds up in your blood, forcing your kidneys to work overtime to filter and absorb the excess sugar. When your kidneys can’t keep up, the excess glucose is excreted into your urine, dragging along fluids from your tissues, which makes you dehydrated.
What to Do:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Avoid sugary drinks, which can raise blood glucose levels.
- Monitor Fluid Intake: Keep track of how much fluid you consume versus how much you urinate. If the frequency of urination seems excessive, consult a healthcare professional.
- Seek Medical Advice: If these symptoms persist, it’s important to get your blood sugar levels checked.
2. Extreme Fatigue
Unexplained fatigue is another common symptom of diabetes. When your body can’t effectively use glucose for energy, you may feel tired all the time.
What to Do:
- Balanced Diet: Focus on a balanced diet that includes complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to help your body use insulin more efficiently.
- Consult a Doctor: Persistent fatigue can indicate that your diabetes is not well-managed or that you need to be tested for the condition.

3. Blurred Vision
High blood sugar levels can cause the lens of the eye to swell, leading to blurred vision. If left untreated, this could lead to more severe complications like diabetic retinopathy.
What to Do:
- Get an Eye Exam: Schedule an eye exam to check for signs of diabetic retinopathy or other eye conditions.
- Control Blood Sugar Levels: Work with your healthcare provider to manage your blood glucose levels and prevent further eye damage.
- Use Proper Eyewear: If you experience blurred vision, make sure you are using the correct prescription glasses or contact lenses.
4. Unexplained Weight Loss
Losing weight without trying can be a sign of diabetes. This occurs because your body starts breaking down muscle and fat for energy when it can’t access glucose.
What to Do:
- Increase Caloric Intake: Consult a dietitian to help you develop a meal plan that provides sufficient calories and nutrients.
- Regular Monitoring: Keep track of your weight and discuss any significant changes with your doctor.
- Medical Evaluation: Unexplained weight loss should always be evaluated by a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause.
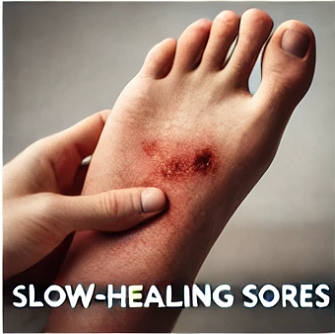
5. Slow-Healing Sores or Frequent Infections
High blood sugar can impair blood flow and immune function, leading to slow-healing sores and frequent infections.
What to Do:
- Proper Wound Care: Keep wounds clean and covered, and monitor them for signs of infection.
- Blood Sugar Control: Maintaining blood glucose within a healthy range can promote better healing.
- See a Specialist: If wounds are not healing or if you develop frequent infections, see a healthcare provider promptly.
6. Tingling or Numbness in Hands and Feet
Nerve damage, known as diabetic neuropathy, can cause tingling, numbness, or pain in your hands and feet.
What to Do:
- Foot Care: Inspect your feet daily for any signs of injury or infection, and wear comfortable shoes that provide good support.
- Physical Therapy: Consider physical therapy to improve circulation and manage pain.
- Discuss Medications: Certain medications can help manage the symptoms of diabetic neuropathy. Consult your doctor about your options.
7. Increased Hunger
People with diabetes often experience polyphagia, or excessive hunger. Even though you are eating, your body may not be getting the energy it needs from the food, leading to increased hunger.
What to Do:
- Eat Small, Frequent Meals: Instead of large meals, eat small, frequent meals to help manage blood sugar levels.
- Focus on Fiber: Foods high in fiber can help you feel full longer and stabilize blood glucose levels.
- Monitor Blood Sugar: Keep an eye on your blood sugar levels, especially after meals, to understand how different foods affect you.
8. Dark Patches of Skin
Dark patches of skin, often velvety in texture, particularly in body folds like the neck, armpits, or groin, can be a sign of insulin resistance, which is a precursor to type 2 diabetes.
What to Do:
- Weight Management: If overweight, losing weight can improve insulin sensitivity.
- Dermatological Consultation: A dermatologist can assess skin changes and recommend treatments to manage them.
- Blood Sugar Testing: Since this could be a sign of prediabetes or diabetes, it’s crucial to get your blood sugar levels checked.
Recognizing the early symptoms of diabetes and taking appropriate action can prevent complications and improve your quality of life. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. Managing diabetes effectively requires a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring.
References
- American Diabetes Association
- Mayo Clinic – Diabetes Symptoms
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
#diabetesawareness #diabetessymptoms #healthtips #diabetescare #healthyliving #bloodsugarcontrol #diabetesmanagement #wellnessjourney #prediabetes #diabeticlife