While managing diabetes can be challenging, there are simple steps you can take to improve your chances of reversing diabetes and its effects. This guide will provide you with practical advice on how to improve your health through diet, exercise, weight management, and other lifestyle changes. By following these steps, you can take control of your diabetes and improve your overall well-being.
Understanding Diabetes
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high levels of glucose in the blood. It occurs when the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. Without proper insulin function, glucose accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to various health issues.
Types of Diabetes
There are two main types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes, the most common form, occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin and is often linked to lifestyle factors and can be managed or even reversed through healthy changes.
Importance of Diet in Reversing Diabetes
Foods to Include
Diet plays a crucial role in managing and reversing diabetes. Including foods that help stabilize blood sugar levels is essential. Focus on consuming a variety of vegetables, especially leafy greens, which are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber. Whole grains, such as quinoa, brown rice, and oats, are better options than refined grains. Incorporating lean proteins, such as chicken, fish, and legumes, can help keep you full and maintain muscle mass. Healthy fats, like those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, are also beneficial.
Foods to Avoid
To reverse diabetes, it’s important to avoid foods that spike blood sugar levels. Steer clear of sugary snacks, beverages, and desserts, which can cause rapid increases in glucose. Processed foods and refined carbohydrates, such as white bread, pastries, and sugary cereals, should be limited. Additionally, be cautious with high-fat foods, especially those containing trans fats, which can contribute to insulin resistance. By making mindful food choices, you can better manage your blood sugar levels and improve your health.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Best Exercises for Diabetes
Regular physical activity is key to reversing diabetes. Engaging in both aerobic exercises and strength training can help. Aerobic exercises, such as walking, jogging, swimming, and cycling, improve cardiovascular health and aid in weight loss. Strength training, like lifting weights or using resistance bands, builds muscle and enhances insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity and two sessions of strength training per week. Consistency is crucial, so find activities you enjoy to stay motivated.
Benefits of Regular Activity
Exercise offers numerous benefits for those managing diabetes. It helps lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity, allowing your cells to use glucose more effectively. Physical activity also aids in weight management, reduces stress, and improves mood. Furthermore, regular exercise can enhance cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of heart disease, which is common among people with diabetes. By incorporating regular physical activity into your routine, you can significantly improve your overall health.
Weight Management
Strategies for Healthy Weight Loss
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for reversing diabetes. Focus on sustainable weight loss strategies rather than quick fixes. Start by setting realistic goals and making gradual changes to your diet and exercise habits. Incorporate more whole foods into your meals and reduce portion sizes. Avoid skipping meals, as this can lead to overeating later. Drink plenty of water and avoid sugary beverages. Tracking your food intake and physical activity can help you stay on track and make informed choices.
Impact of Weight on Diabetes
Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, is a major risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. Fat cells in the abdominal area produce hormones that can lead to insulin resistance. By losing weight, you reduce the amount of fat in your body, which can help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% of your body weight can have a significant impact on your health. Prioritizing weight management can lead to better diabetes control and overall well-being.
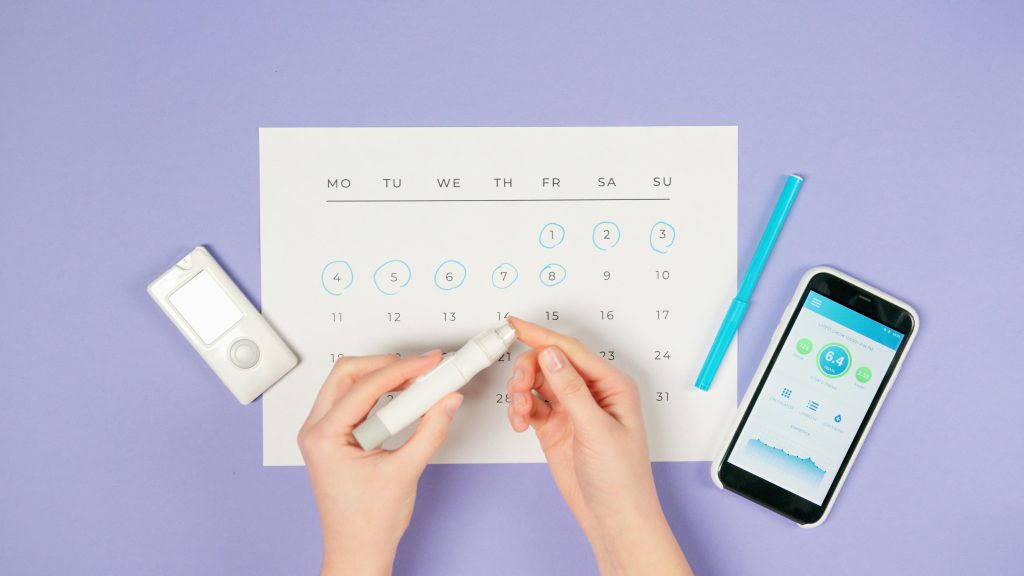
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
How to Monitor at Home
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for managing diabetes. Home glucose meters are widely available and easy to use. To check your blood sugar, wash your hands, insert a test strip into the meter, and use the lancet to prick your fingertip. Apply a drop of blood to the test strip and wait for the meter to display your blood sugar level. Keep a log of your readings to track patterns and identify any changes. Monitoring helps you make informed decisions about your diet, exercise, and medication.
Importance of Regular Testing
Regular blood sugar testing provides valuable insights into how your body responds to different foods, activities, and medications. It helps you understand what works best for managing your diabetes. Consistent monitoring can prevent complications by allowing you to catch and address high or low blood sugar levels early. Discuss your target blood sugar range with your healthcare provider and follow their recommendations on when to test. By staying vigilant, you can maintain better control over your diabetes.
Stress Management
Techniques to Reduce Stress
Managing stress is an important aspect of reversing diabetes. Chronic stress can raise blood sugar levels and make diabetes management more difficult. Incorporate stress-reduction techniques into your daily routine. Practice mindfulness and meditation to calm your mind. Engage in activities you enjoy, such as reading, gardening, or listening to music. Regular physical activity, like yoga or tai chi, can also reduce stress. Deep breathing exercises and progressive muscle relaxation are simple methods to help you unwind.
Effect of Stress on Blood Sugar
Stress triggers the release of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can increase blood sugar levels. For people with diabetes, this can lead to fluctuations that are difficult to manage. Chronic stress can also lead to poor lifestyle choices, such as unhealthy eating and reduced physical activity. By effectively managing stress, you can stabilize your blood sugar levels and improve your overall health. Prioritizing stress management is a key component of a comprehensive diabetes reversal plan.
Sleep and Diabetes
Importance of Quality Sleep
Getting quality sleep is vital for managing and reversing diabetes. Poor sleep can affect your body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels and increase insulin resistance. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night. Establish a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same times each day. Create a relaxing bedtime routine to help signal your body that it’s time to wind down. Avoid caffeine and electronic devices before bed to improve your sleep quality.
Tips for Better Sleep
To enhance your sleep quality, create a comfortable sleep environment. Ensure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet. Invest in a good mattress and pillows that provide adequate support. Limit naps during the day to avoid disrupting your nighttime sleep. Incorporate relaxing activities before bed, such as reading or taking a warm bath. If you have trouble sleeping, consider talking to your healthcare provider for further advice. Improving your sleep can have a positive impact on your diabetes management.
Reversing diabetes is possible with dedication and the right approach. By making simple changes to your diet, incorporating regular exercise, managing your weight, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, you can improve your blood sugar levels and overall health. Regular monitoring, stress management, and quality sleep are also essential components of effective diabetes control. Remember, consistency is key, and small, gradual changes can lead to significant improvements over time. Take charge of your